video-based pose transfer method
Dance Dance Generation: Motion Transfer for Internet Videos
该文章可以实现在复杂背景下的pose transfer。
In summary, our contributions include the following.
-
We demonstrate personalized motion transfer on videos from the Internet.
-
We propose a novel two-stage frame-work to synthesize people performing new movements and fuse them seamlessly with background scenes. (主要贡献:实现复杂背景下的姿态转换)
-
We perform qualitative and quantitative evaluations validating the superiority of our method over existing state-of-the-art.


method: (主要的思想是先将利用语义分割图将前景中的人物进行分割,采用STN 将前景人物与目标人物进行对齐。随后通过第二阶段进行修正)
- 利用语义分割图将前景中的人物进行分割,采用STN 将前景人物与目标人物进行对齐。
- Human synthesis net:将对齐的body parts与target pose 作为输入,对body parts进行修正,并得到前景mask
- fusion net:将body parts + background +target pose 作为输入,进行前景和背景的融合,实现复杂背景下的pose transfer
这里需要注意的点:
-
如何保证生成视频帧在时间上是平滑的?方法: target pose采用多帧的姿态表示作为输入。

存在的问题:
当source person和target person将的body shape 存在较大差异时,可能生成的结果就不那么理想了。
TransMoMo: Invariance-Driven Unsupervised Video Motion Retargeting

难点:
1.原图像和目标图像间存在较大的结构和视角变化
2.难以构建合适的训练对进行训练
3.human motion的变化是复杂的。
解决思路:
三阶段网络:(这使得我们能够更加的关注motion retarget,其中步骤1,步骤3是直接采用现有最好的方法即可)
1.skeleton extraction
2.motion retarget(主要贡献处:invariance-driven disentanglement)
3.skeleton-to-video rendering
为了解决第2和第3个难点,利用了三个因素的不变性质:structure(表示体型),motion(表示姿态),view-angle(表示相机视角)。具体来说:
1.当structure 和 view-angle变化时,motion是不变的
2.当view-angle变化时,structure是不变的,同时structure不会随着时间的变化而变化
3.当structure变化时,view-angle是不变的,同时view-angle不会随着时间的变化而变化
这些不变特性使得我们能够设计一些无监督函数来将skeleton解耦成三个正交的隐变量:structure,motion,view-angle。
可以通过mix来自不同skeleton的structure(原图像的structure,即原人物体型)和motion(目标图像的motion,即目标姿态)来实现motion retarget; 通过在decoder阶段采用不同的view-angle来实现不同视角下的motion retarget
网络结构:

具体的实施步骤:
- 通过现有的姿态提取器提取source video中人物姿态(多帧)以及提取target video中人物姿态(多帧)。
- motion retarget network中由encoder 和 decoder组成,encoder将skeleton通过三个独立的解码器进行解码,得到view-angle code 、motion code和structure code。
- [将source video中的motion code和target video 中的 structure code结合以及任取一个view-angle code(用于实现视角变化] 经过decoder进行解码,得到一个3D的,可以具有不同视角的 Retargeted skeleton code ,最后再将这个3D Retargeted skeleton code映射为2D Retargeted skeleton
- 将和 target video中人物的纹理通过skeleton-to-video rendering渲染到Retargeted skeleton 上。实现motion transfer task
在motion retarget network中的网络细节:
输入是一个skeleton 序列(多帧):$x \in \mathbb{R}^{T \times 2N}$ 。$T$表示帧数,$N$表示骨骼点。encoder分为三个部分
-
motion encoder: 结构:several layers of one dimensional temporal convolution 。输出$E_m(x)=m \in \mathbb{R}^{M \times C_m}$。$M$表示帧数,$C_m$表示通道数
-
structure encoder:结构:several layers of one dimensional temporal convolution+ temporal max pooling。输出:$\bar{E}_s(x)=\bar{s} \in \mathbb{R}^{C_s} =pool(s)$ 其中 $E_s(x)=s \in \mathbb{R}^{M \times C_s}$
-
view-angle encoder: 结构:several layers of one dimensional temporal convolution+ temporal max pooling。输出:$\bar{E}_v(x)=\bar{v} \in \mathbb{R}^{C_v} =pool(s)$ 其中 $E_v(x)=v \in \mathbb{R}^{M \times C_v}$
-
将$m,\bar{s},\bar{v}$进行组合,经由decoder得到3D Retargeted skeleton code:${\large{\hat{X}}}=G(m,\bar{s},\bar{v}) \in \mathbb{R}^{T \times 3N}$
本文的关键点在于如何确保通过motion retarget network提取的structure(表示体型),motion(表示姿态),view-angle(表示相机视角)是解耦的。(skeleton -> structure,motion,view-angle)
-
结构变化处理:
将输入的skeleton进行缩放处理。

-
视角变化处理:
将输入的skeleton进行360度视角转换

现在要通过loss term保证前面提到的三个不变特性:
1.当structure 和 view-angle变化时,motion是不变的
2.当view-angle变化时,structure是不变的,同时structure不会随着时间的变化而变化
3.当structure变化时,view-angle是不变的,同时view-angle不会随着时间的变化而变化
-
1. Invariance of motion
- Cross Reconstruction Loss


- Structural Invariance Loss

- Rotation Invariance Loss

-
2.Invariance of Structure
- Triplet Loss(确保structure 不随时间变化,这个不太理解)

- Rotation Invariance Loss

-
3.Invariance of View-Angle
- Triplet Loss(确保view-angle不随时间变化,这个不太理解)

- Structural Invariance Loss

可能存在的一些问题:
仅仅从skeleton的角度进行处理,并没有显示的考虑纹理信息(即没有考虑skeleton与纹理之间的对齐问题)。从这一角度出发是不是可以进行优化?
生成结果的时间连续性上的处理是采用多帧的skeleton进行输入。
Deep Spatial Transformation for Pose-Guided Person Image Generation and Animation
该文首先基于图像设计了一种新颖的网络框架,随后又将其拓展到视频生成(主要加上了skeleton降噪处理时间平滑性处理)
这里只介绍video-based person generation
第一部分为skeleton的降噪处理。
作者认为通过现有方法(如openpose)提取出来的skeleton的表示并不精确,因此首先对提取出来的skeleton进行降噪处理

第二部分为视频帧时间平滑处理

- 将source image(将source image根据目标姿态进行warp和前一帧的输出(将前一帧的输出根据目标姿态进行warp)共同作为当前帧生成网络的输入
针对source image 和 前一帧的输出使用独立的模块。最后再将两者的输出相加作为当前帧的输出。

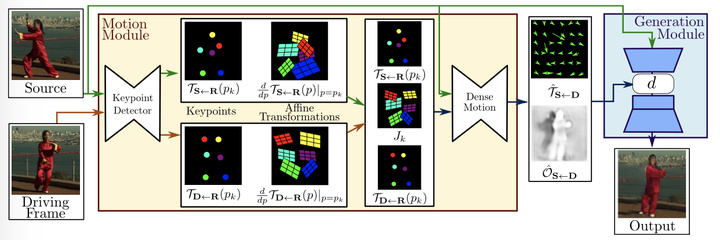
First Order Motion Model for Image Animation
Method
FOMM使用了相邻关键点的局部仿射变换来模拟物体运动,还额外考虑了遮挡的部分,遮挡的部分可以使用image inpainting生成。
参数定义:
- $S$:原图像
- $D$:驱动帧
- $\mathcal{T}_{S\leftarrow D}$:后向光流场,建立$D$与$S$中每一个像素位置的对应关系.–>就是预测一个仿射变换
- $R$:中间参考帧
首先因为没有完美的监督信息,所以文章借鉴了monkey-net的训练方法:用同一个视频同时作为source image和driving video来利用本身作为监督信息,这类似于一种自监督的学习机制。然后文章提出的方法大概包括以下模块:
keypoint detector
keypoint detector会输出关键点信息和局部仿射变换的参数信息,这些参数使得关键点附近的姿态信息可以通过局部仿射变换得到,然后通过泰勒展开可以得到 $T_{X\leftarrow R}$,其中$X=S$或$X=D$.
Local Affine Transformations for Approximate Motion Description
在推断过程中,D和S的关键点差异可能会比较大,所以作者引入了一个抽象的参考帧R,通过预测R到S的映射 $T_{S\leftarrow R}$和R到D的映射$T_{D\leftarrow R}$ ,这样避免了直接计算D到S的映射,并且可以同时处理D和S。在通过这种方法得到 $T_{S\leftarrow R}$和$T_{D\leftarrow R}$ ,并联合原图像$S$送入motion estimation module中的dense motion network,得到对应的输出$T_{S\leftarrow D}$和$\mathcal{O}_{S\leftarrow D}$.
这个部分的理解我们首先需要考虑一个非常简单的问题:如何用一种最naive的方法来借助driving video中的关键点帮助调整source image中的motion?这个问题的解答可能会让人想到一种简单的映射函数:R2->R2,也就是将一个帧里的像素映射到另一帧里面去,这种思想非常类似于inpainting里面的examplar的方法:像素迁移,这种映射关系在光流场中被称为后向光流场。
但是作者没有直接地将D映射到S,而是假设了一种中间的reference帧来帮助建立过渡关系,这一篇的独到之处在于用local affine transformations来逼近运动的表述,也就是用泰勒展开来逼近于关键点在空间的位移,关键点和仿射系数都是由关键点检测的网络来输出。
我对于这一步的理解其实很像光流的计算原理:
也就是说可以用关键点的位置加上一个映射的仿射系数和无穷小量来表示运动之后的关键点的位置,其中关键点就是当前的位置信息,然后映射系数就是motion信息,最后无穷小量可以被忽略不计。
$$ \mathcal{T}{\mathbf{X} \leftarrow \mathbf{R}}(p)=\mathcal{T}{\mathbf{X} \leftarrow \mathbf{R}}\left(p_{k}\right)+\left(\left.\frac{d}{d p} \mathcal{T}_{\mathbf{X} \leftarrow \mathbf{R}}(p)\right|_{p=p_{k}}\right)\left(p-p_{k}\right)+o\left(\left|p-p_{k}\right|\right) $$
$$ \mathcal{T}{\mathbf{X} \leftarrow \mathrm{R}}(p) \simeq\left{\left{\mathcal{T}{\mathbf{X} \leftarrow \mathbf{R}}\left(p_{1}\right),\left.\frac{d}{d p} \mathcal{T}_{\mathbf{X} \leftarrow \mathrm{R}}(p)\right|_{p=p_{1}}\right}, \ldots\left{\mathcal{T}_{\mathbf{X} \leftarrow \mathbf{R}}\left(p_{k}\right),\left.\frac{d}{d p} \mathcal{T}_{\mathbf{X} \leftarrow \mathrm{R}}(p)\right|_{p=p_{K}}\right}\right} $$
$$ \mathcal{T}{\mathrm{S} \leftarrow \mathrm{D}}=\mathcal{T}{\mathrm{S} \leftarrow \mathrm{R}} \circ \mathcal{T}{\mathrm{R} \leftarrow \mathrm{D}}=\mathcal{T}{\mathrm{S}} \leftarrow \mathrm{R} \circ \mathcal{T}{\mathrm{D} \leftarrow \mathrm{R}}^{-1} $$ After computing again the first order Taylor expansion of Eq. (3) (see Sup. Mat.), $$ \mathcal{T}{\mathbf{S} \leftarrow \mathrm{D}}(z) \approx \mathcal{T}{\mathbf{S} \leftarrow \mathbf{R}}\left(p{k}\right)+J_{k}\left(z-\mathcal{T}_{\mathbf{D} \leftarrow \mathbf{R}}\left(p_{k}\right)\right) $$ with: $$ J_{k}=\left(\left.\frac{d}{d p} \mathcal{T}_{\mathrm{S}} \leftarrow \mathrm{R}(p)\right|_{p=p_{k}}\right)\left(\frac{d}{d p} \mathcal{T}_{\mathrm{D}} \leftarrow \mathrm{R}(p) \mid p=p_{k}\right)^{-1} $$
只预测仿射变换对应零阶 也就是monkeynet , 加上雅可比矩阵之后 也就是对应一阶 对应这篇文章的idea 我觉得零阶就认为关键点附近的物体运动是一致的,一阶就是关键点附近的形变可以有一定的不一致
当然这一步我觉得是需要基于一个物理假设的就是每一个关键点对应的一个刚体,其上的运动是一样的,然后就是可以用泰勒展开的方法来逼近这个刚体部分的运动。(文章提到了monkey-net其实就是只用了零阶的泰勒展开,而本文进一步优化提出了一阶的泰勒展开)
Occlusion-aware Image Generation
第二步是由上一步预测得到的关键点和仿射系数来预测一个更加dense的光流场变化,并输出一个occlusion mask来指示哪个区域直接transfer哪个区域需要inpainting。
然后就是生成器首先用上一步预测得到的dense的光流场来warp source图像,并结合那些occlusion的区域进行inpainting得到最终的输出。
DwNet: Dense warp-based network for pose-guided human video generation


Cross-Identity Motion Transfer for Arbitrary Objects Through Pose-Attentive Video Reassembling
贡献:


基于warp的方法能够解决解决较小的形变问题,但是还是存在一下几点问题:
1.难以构建大的、复杂的位移
2.不能够使用多个原图像进行生成(使用多个原图像同时进行生成可以起到相互补充的作用)
之前的方法仅仅使用一张原图像进行生成。当原图像和目标图像之间存在较大的形变时,就会出现生成图像和目标图像之间无法存在一一对应的关系,导致生成的结果差;通过使用多张原图像可以起到相互补充的作用(可以利用多张原图像的外观)
采用交叉训练的方式,这能够使其进行不同外观物体之间的motion transfer


Pose-Dependent Appearance Embedding
提取图像的姿态编码和外观编码

Pose-Attentive Retrieval Block
使用注意力机制来融合多个原图像的外观信息

Image Generation
考虑背景的影响,单独使用一个自编码器学习背景信息。最后再将其融合进前景中

训练方式
训练方式分为了重构训练和交叉训练

重构损失

交叉损失

总的损失函数

推理阶段

本文存在的最大的一个问题在于是一张一张的生成图像,并没有考虑帧与帧之间的连续性,即一帧一帧的生成图像->可以考虑处理帧与帧之间的连续性
还有一个问题就是只在一个维度的特征空间中进行attention的融合,可以考虑多维度的融合